https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/eco-friendly-packaging-for-medicines-in-glass.jpg
654
1154
SFAM
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/logo-sfam.svg
SFAM2025-09-11 17:19:452025-09-11 17:19:45Eco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glass
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/eco-friendly-packaging-for-medicines-in-glass.jpg
654
1154
SFAM
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/logo-sfam.svg
SFAM2025-09-11 17:19:452025-09-11 17:19:45Eco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glassEco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glass
Pharmaceutical packaging must meet strict requirements in terms of safety, sterility, and traceability. But in recent years, another dimension has emerged: sustainability. By 2025, eco-design is becoming a strategic priority for the pharmaceutical industry.

Pharmaceutical packaging must meet strict requirements in terms of safety, sterility, and traceability. But in recent years, another dimension has emerged: sustainability. By 2025, eco-design is becoming a strategic priority for the pharmaceutical industry.
Driven by societal trends towards sustainability, as well as by regulations and environmental targets, industry players must rethink their choice of materials and manufacturing processes. Ecological and infinitely recyclable, glass offers a sustainable and safe alternative to traditional plastic packaging.
In this article, we explore the trends and challenges of eco-designed packaging for the pharmaceutical industry.
1. The emerging trends in eco-design in the pharmaceutical sector
a. Eco-design: A major strategic challenge for the industry in 2025
The eco-design of pharmaceutical packaging has now become a key condition for competitiveness, driven not only by societal expectations but also by profitability. On the one hand, patients are increasingly sensitive to environmental issues and seek more eco-responsible solutions. On the other hand, investors and partners are also demanding clear commitments to sustainable development. As a result, it is crucial for manufacturers to integrate sustainability criteria right from the design stage of their packaging.
b. Concrete practices in pharmaceutical packaging eco-design
In the pharmaceutical sector, eco-design is reflected through several concrete actions:
- Reducing packaging weight and volume: this limits the amount of raw material required.
- Logistical and energy optimisation: helping reduce the carbon footprint of supply chains.
- Integrating life cycle assessment (LCA) into design processes: his approach provides a comprehensive view of environmental impact, from production to end-of-life.
2. Glass: A sustainable material suited to pharmaceutical packaging
a. The ecological advantages of glass in pharmaceutical packaging design
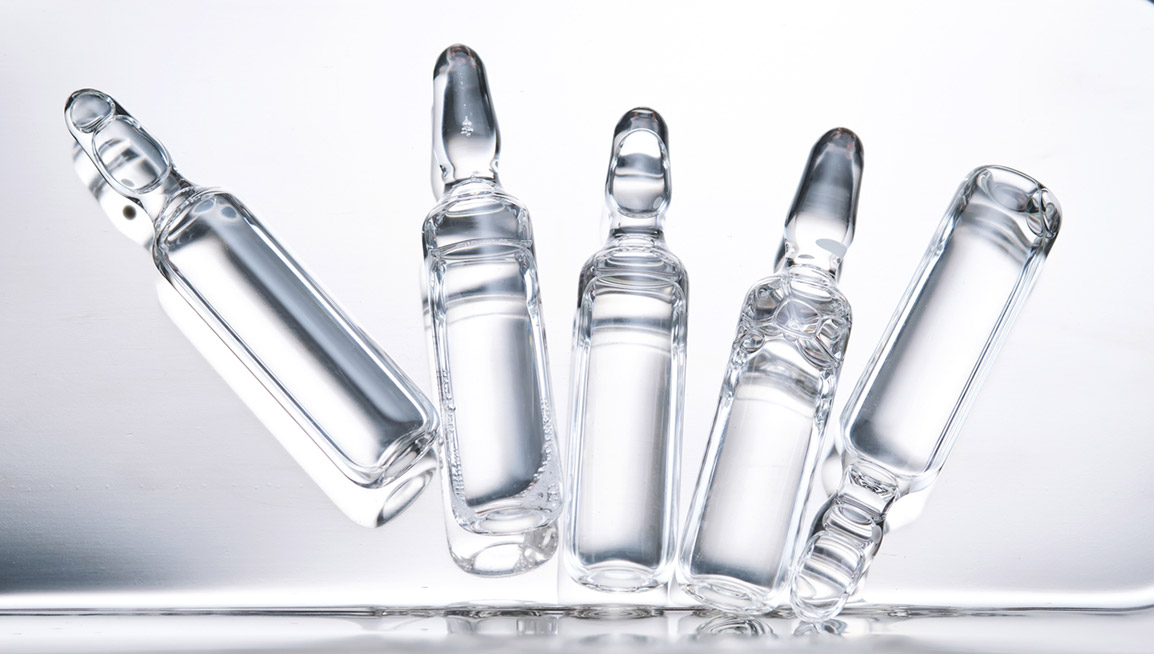
Glass is recognized as an ecological material. It is 100% recyclable and infinitely reusable without any loss of quality. It does not release harmful substances and does not generate lasting pollution in the environment.
Unlike certain plastics, it contains neither endocrine disruptors nor risky additives. Its chemical inertness makes it an ideal solution for safe, sustainable pharmaceutical packaging.
b. Performance and safety of glass for the pharmaceutical industry
Beyond its sustainability advantages, glass offers essential technical properties for pharmaceutical packaging in eco-designed medicines. It provides high chemical and thermal stability, interacts minimally with active ingredients, and ensures effective protection for sensitive formulations.
Type I glass (borosilicate, high resistance) and Type III glass (soda-lime glass) comply with the strict requirements of the European Pharmacopoeia. These qualities explain why glass is the preferred choice for packaging injectable medicines and liquid dietary supplements.
Glass is an ideal material for eco-designed pharmaceutical packaging. To learn more about the different types of pharmaceutical glass, read our full article.
3. Regulatory requirements and the future of sustainable pharmaceutical packaging
a. Increasingly demanding regulations
European regulations are evolving to integrate environmental criteria. The European Union is encouraging the replacement of plastics with more sustainable and recyclable materials. Directives such as the European Green Deal and packaging regulations are imposing new requirements on manufacturers. Pharmaceutical packaging is no exception to this transformation: industry players must now take these regulations into account and ensure the sustainability of their solutions.
b. An opportunity for industry players
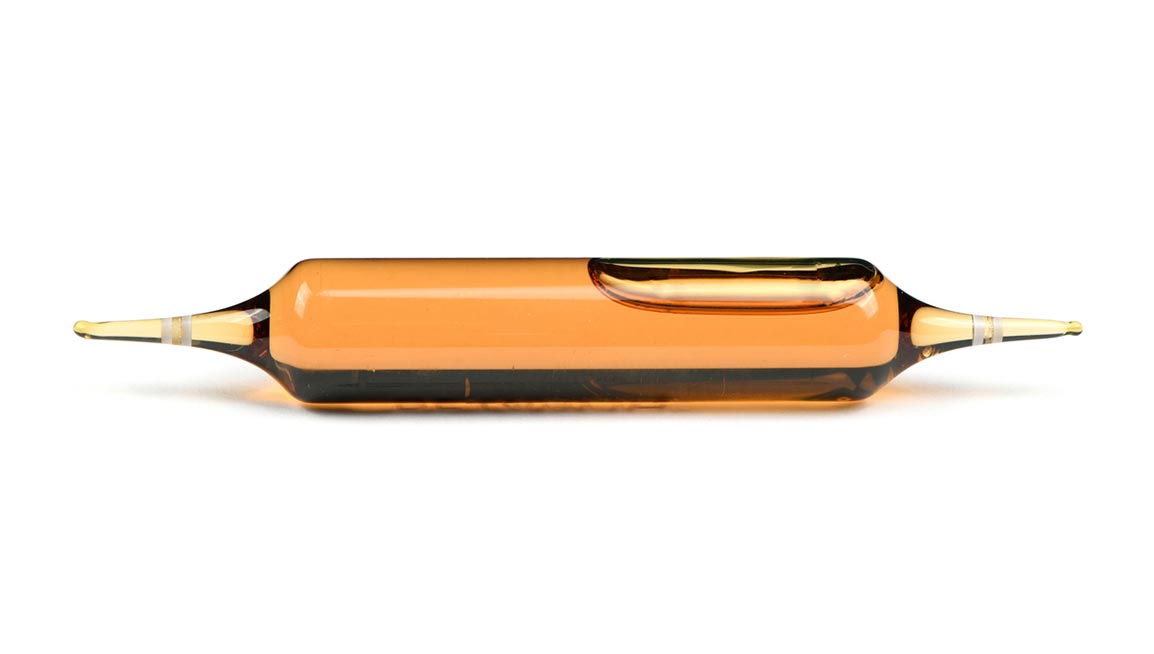
This regulatory shift also represents a strategic opportunity. Manufacturers that succeed in integrating eco-design into their packaging development and communicating about their responsible material choices gain a competitive edge in a crowded market. And while glass already meets the environmental and health expectations of sustainable pharmaceutical packaging, few players highlight its eco-design in their strategy. The double-tip glass ampoule can therefore prove to be a strategic choice for eco-designed packaging.
To learn more about the manufacturing of double-tip glass ampoules, read our full article.
4. Innovation and responsibility of manufacturers in eco-design
a. The central role of technological innovation
Innovation is a key driver in reconciling industrial performance with sustainability. Modern production lines are automated to reduce energy consumption and minimize material waste. Automated quality controls ensure consistent compliance while lowering rejection rates. Patents filed by manufacturers, such as those related to vacuum filling, glass heat treatment, or SFAM’s Double Ring Break (DRB) pre-scoring system illustrate the industry’s ability to enhance the safety, sustainability, and efficiency of pharmaceutical packaging.
b. Manufacturers’ responsibility in meeting customer expectations
Pharmaceutical laboratories and dietary supplement brands are seeking reliable, compliant, and more environmentally friendly solutions. Packaging manufacturers must anticipate these expectations by offering designs that meet regulatory requirements while integrating eco-design criteria. The double-tip glass ampoule, produced in France and certified, stands as an example of eco-responsible pharmaceutical packaging.
Pharmaceutical packaging is entering a new era, where eco-design and sustainability are becoming essential. Highly recyclable and safe, glass is establishing itself as a benchmark solution to meet environmental and regulatory expectations. Double-tip glass ampoules and crushable ampoules are favoured for their eco-design, while the continuous optimisation of manufacturing processes helps reduce the carbon footprint and strengthen the circular economy. Manufacturers able to combine technology, quality, and sustainability throughout their development and production chain will become strategic partners for players in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical markets.