https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/eco-friendly-packaging-for-medicines-in-glass.jpg
654
1154
SFAM
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/logo-sfam.svg
SFAM2025-09-11 17:19:452025-09-11 17:19:45Eco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glass
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/eco-friendly-packaging-for-medicines-in-glass.jpg
654
1154
SFAM
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/logo-sfam.svg
SFAM2025-09-11 17:19:452025-09-11 17:19:45Eco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glassHow to start a pharmaceutical company: a comprehensive guide
Starting a business in the pharmaceutical industry requires careful planning, an understanding of strict regulations, and significant investments.
In this article, you will find what you need to know about the steps to start a pharmaceutical company.

Starting a business in the pharmaceutical industry requires careful planning, an understanding of strict regulations, and significant investments.
In this article, you will find what you need to know about the steps to start a pharmaceutical company.
1. Steps to start a pharmaceutical company
a. Market study
The first step in starting a pharmaceutical company is to conduct a thorough market study, identifying unmet needs in the industry and assessing the competition. Market segmentation will help you focus on specific areas such as pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, or biotechnologies.
The choice of segment will determine your research and development (R&D) strategy, as well as your infrastructure and financing requirements.
b. Strategic planning
Once the market study has been completed, the next step is to define your objective and the strategy to achieve it. Will you focus on generic drugs with cost-efficient production, or on highly innovative products requiring significant R&D investments ? These are two distinct approaches that will shape your decisions regarding technologies, equipment, and industrial partnerships.
c. Choice of segment
Patented drugs require significant investments in R&D and clinical trials. Although they are less expensive to develop, generic drugs demand mastery of large-scale production. As for dietary supplements, while they are subject to less stringent regulations, the competition is intense, making differentiation through quality and innovation essential.
2. Choice of products and technologies
Several factors influence the choice of products to develop: innovation, development costs, and market potential.
- Patented drugs: they offer high margins, but their development is long and costly.
- Generics: they enable faster market entry, but competition is tougher.
- Biotechnologies: they play an increasingly important role in the pharmaceutical industry, enabling the development of innovative treatments (immunotherapy, gene therapies, etc.). These technologies are particularly attractive to startups seeking to position themselves in high value-added niches, but they require access to substantial financing.
To find out more on pharmaceutical manufacturing of medications, discover our complete article.
3. Financing and business plan
Financing is one of the biggest challenges in setting up a pharmaceutical company. The cost of developing a drug, from initial research to market launch, can lead to millions of euros.
The development of a solid business plan is therefore essential to convince the various types of investors such as:
- Private investors (business angels, venture capital funds),
- Public investors (public subsidies),
- Industrial partners (fundraising).
The business plan must include detailed financial projections, such as:
- R&D costs,
- Production costs,
- Costs related to clinical trials,
- Marketing expenses.
It is important to estimate the return on investment over several years, taking into account the long approval periods (Marketing Authorization-MA) for pharmaceutical products. To learn everything about MA, discover our complete MA guide.
4. The standards and certifications to comply with
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most strictly regulated industries in the world.
In France, for example, standards include:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): covering all stages of production, from the manufacturing of raw materials to the distribution of finished products, with rigorous controls, throughout the process.
- The European Pharmacopoeia: pharmaceutical companies must comply with the requirements of the European Pharmacopoeia, which regulates the quality standards of medicines in Europe.
- The ISO certifications: ISO standards (ISO 9001, ISO 15378…) are often required to ensure compliance with international standards and facilitate the export of products.
Find more information on iso pharmaceutical norms in our dedicated guide.
5. Infrastructure and production
Pharmaceutical production requires specific infrastructures, including research laboratories, manufacturing plants that comply with GMP standards, and advanced equipment. Automating production lines helps optimize productivity and control costs.
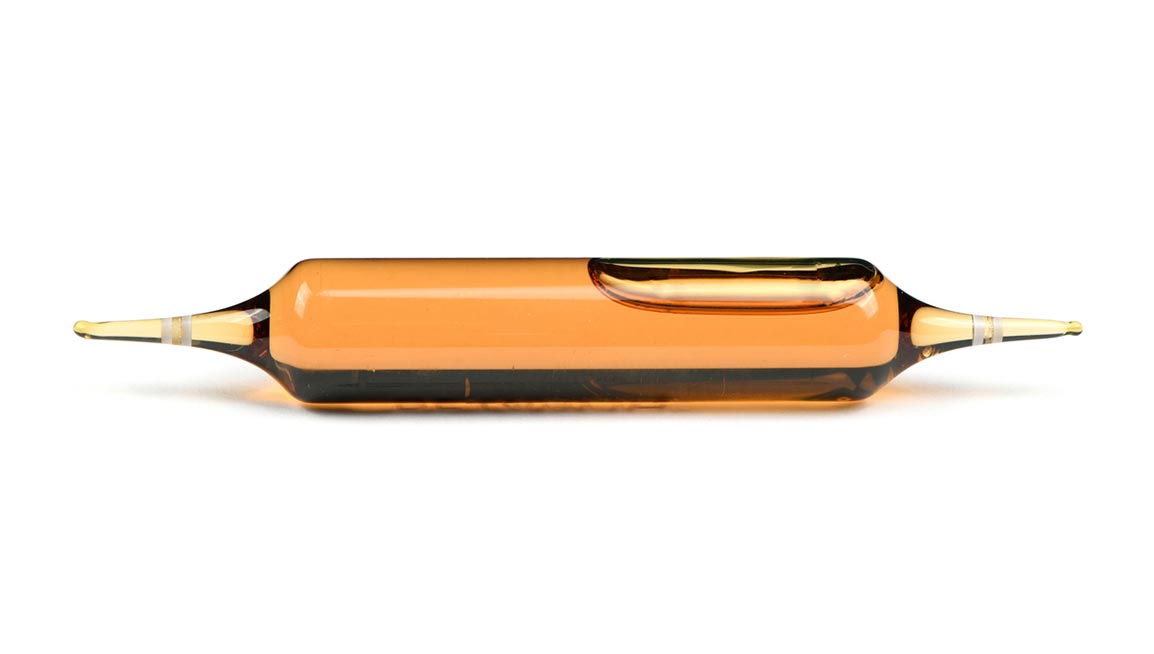
At SFAM, we design double-tip ampoules with some of the most competitive filling costs on the market, to help you manage your costs.